Frames of Reference, Position, Path Length and Displacement
Frames of Reference, Position, Path Length and Displacement: Overview
This topic highlights the definition of reference point, path length and displacement. We will learn how to determine the position of a body in space. It also covers the difference between path length and displacement via examples.
Important Questions on Frames of Reference, Position, Path Length and Displacement
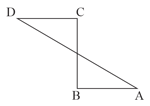
A boy moves from A to B through , B to C through and again from C to D through . Find his displacement.
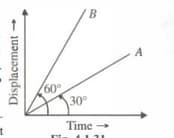
Two starlight lines drawn on the same displacement time graph make angles and with time axis respectively. Which line represents greater velocity? What is the ratio of two velocities?
What is the distance in of a quasar from which light takes years to reach the earth? The speed of the light .
The average velocity of a particle is equal to its instantaneous velocity. What is the shape of the displacement-time graph?
Is it possible that a body is at rest and at the same time is in motion?
What is a point object?
Rest and motion are relative terms. Explain with two examples.
The average velocity of a particle is zero during some interval of time. What is the displacement of the particle during that time interval?
A body is moving along a circular path. When it completes on rotation what is the displacement travelled of the body?
A body is moving along a circular path. When it completes on rotation what is the distance travelled of the body?
Give an example of a body for which there is a change in position, but displacement is zero?
" Distance travelled by a body can not be negative ". Why?
" Motion of the planet around the sun in its orbit is considered as an example of two-dimensional motion," why?
Under what condition can we treat a train as a point object?
While dealing with translatory motion of extended bodies why do we treat them as point object?
Give an example of a body which is at rest with respect to one body, but is in motion with respect to another.
What is point mass with gravity?
What is point mass give examples?
What is the concept of a point object?
What is the concept of point mass with suitable example?